On Nov 5, 2018, Prof. Hai Song’s laboratory published a research paper on EMBO Journal entitled “Loss of VGLL4 suppresses tumor PD-L1 expression and immune evasion”. This study revealed the critical role of VGLL4 in anti-tumor immunity and the underlying mechanisms.
Evasion of immune surveillance is a hallmark of cancer, which enables tumor cells to escape the attack from immune cells. The recent breakthroughs in the discovery of cancer immune checkpoints such as PD-L1 (also known as B7-H1 or CD274) and the success of checkpoint inhibitors in stimulating anti-tumor immune response have opened an avenue in the understanding of tumor immunology and the development of new strategy for cancer therapies. Understanding the regulatory mechanism of PD-L1 and PD-1 will improve the clinical response rate and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in cancer patients and the development of combinatorial strategies. Hippo pathway is first discovered in Drosophila and involved in organ-size control, tissue homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Several studies identified VGLL4 as a transcriptional suppressor that inhibits YAP-induced overgrowth and tumorigenesis through direct competition with YAP for binding to TEADs. Recently, the effects of the Hippo pathway components on tumor initiation and growth in the context of reciprocal interactions between tumor cells and host anti-tumor immune responses have emerged. However, whether VGLL4 has a role in anti-tumor immunity is largely unknown.
In this study, the authors found that disruption of Vgll4 results in potent T cell-mediated tumor regression in murine syngeneic models. VGLL4 deficiency reduces PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. VGLL4 interacts with IRF2BP2 and promotes its protein stability through inhibiting proteasome-mediated protein degradation. Loss of IRF2BP2 results in persistent binding of IRF2, a transcriptional repressor, to PD-L1 promoter. In addition, YAP inhibits IFNγ-inducible PD-L1 expression partially through suppressing the expression of VGLL4 and IRF1 by YAP target gene miR-130a. This study identifies VGLL4 as an important regulator of PD-L1 expression and highlights a central role of VGLL4 and YAP in the regulation of tumor immunity.
Dr. Ailing Wu in Prof. Song’s group is the first author. Prof. Song is the corresponding author of this article.This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China to HS.
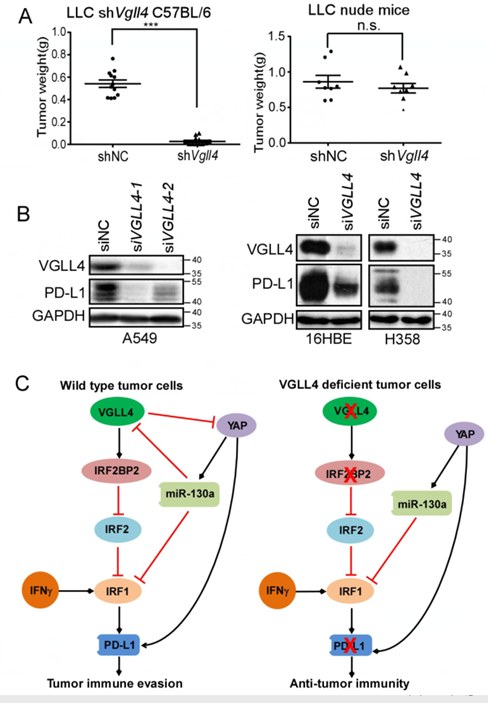
Figure legend. A. Downregulation of Vgll4 in LLC cells strongly inhibits tumor growth in C57BL/6 mice, but not in nude mice. B. Downregulation of VGLL4 suppresses PD-L1 expression in human lung cancer cells. C. Model for the regulation of PD-L1 expression by VGLL4 and YAP. VGLL4 regulates PD-L1 expression through controlling IRF2BP2 protein stability. YAP represses IFNγ-inducible PD-L1 expression partially through miR-130a-mediated inhibition of VGLL4 and IRF1 expression.