On September 20, 2024, the Xu laboratory published TBK1-Zyxin signaling controls tumor-associated macrophage recruitment to mitigate antitumor immunity in The EMBO Journal. This study identified TBK1-Zyxin signaling as a novel mechanism downstream of nucleic acid sensing that regulates macrophage adhesion and motility, which revealed an interesting and critical role of the TBK1-Zyxin axis in controlling tumor-associated macrophage recruitment and its impact on antitumor immunity.
Innate nucleic acid sensing is a crucial immune signaling mechanism for perceiving tissue damages and abnormalities, which are considerably involved in host defense, tumor immunity, organ fibrosis, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative disease. However, it remains unknown whether nucleic acid sensing can directly control the mechanical activity of macrophages. The regulatory mechanism of adhesion and motility of tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment is also unclear. Xu's lab discovered that nucleic acid sensing regulated the adhesion and motility of macrophages. Kinase TBK1 of the cGAS-STING and RLR-MAVS signaling could directly phosphorylate Zyxin at the S143 site in STING or MAVS signalosomes, promoting the recruitment of Zyxin to focal adhesions. Activating the cGAS-STING pathway in TAMs in the tumor microenvironment enhanced Zyxin S143 phosphorylation, while genetic or pharmacological inhibition of the TBK1-Zyxin signaling reduced the infiltration of CD11b+ F4/80+ tumor-associated macrophages, and promoted PD-1-mediated antitumor immunotherapy.
This study first revealed that, beyond its traditional role in pathogen detection and immune activation, nucleic acid sensing also regulated macrophage adhesion and motility. Understanding TBK1-Zyxin signaling and its effect on tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and antitumor immunity would provide new therapeutic targets and theoretical foundations for developing cancer immunotherapies.
Ruyuan Zhou, Mengqiu Wang, and Xiao Li are the first authors. Prof. Pinglong Xu is the corresponding author. This study was collaborated by Prof. Xiaojian Wang, Jian Zou, Tingbo Liang, Xin-Hua Feng, Jian-Zhong Shao, Bing Xia, Dante Neculai, Qi Zhang, and other colleagues, and sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the NSFC Projects, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The study was carried out and completed at Zhejiang University.
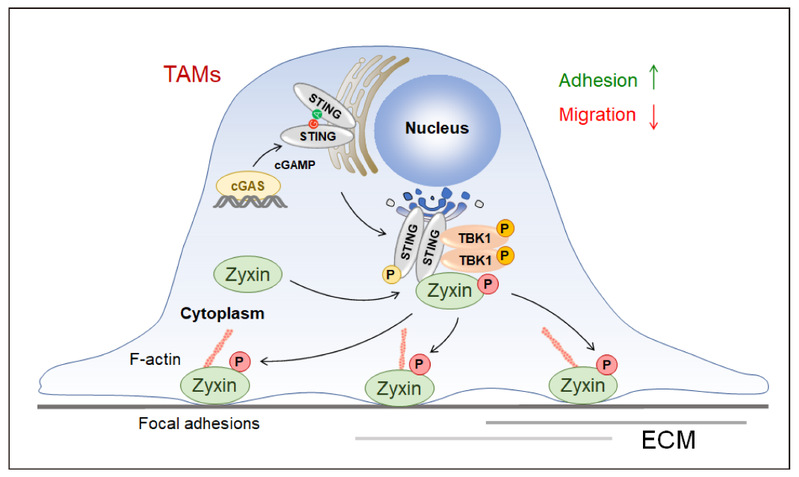
Figure: TBK1-Zyxin signaling controls tumor-associated macrophage
recruitment to mitigate antitumor immunity.
Link: https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.1038/s44318-024-00244-9